Assessment of impact of health education on non communicable diseases on knowledge of intermediate college students
Kumar D.1, Vikramaditya B.2*, Shankar Joshi H.3, Kumar Jha A.4, Manjeeta.5
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijphr.2019.i2.05
1 Deepak Kumar, Junior Resident (Academic), Department of Community and Family Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Science, Rishikesh, Uttarakhand, India.
2* Bibhava Vikramaditya, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SMMH Government Medical College, Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
3 Hari Shankar Joshi, Professor and Head, Department of Community Medicine, SMMH Government Medical College, Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
4 Amit Kumar Jha, Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SMMH Government Medical College, Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
5 Manjeeta, Junior Resident, Department of Community Medicine, SMMH Government Medical College, Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
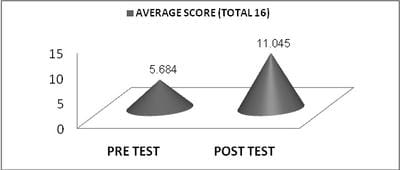
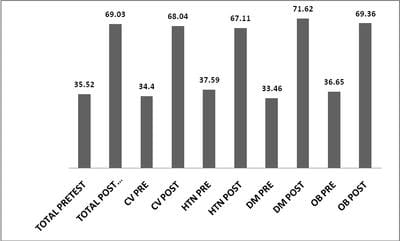
Introduction: There has been a rapid rise in the prevalence of non communicable diseases. Still there is ignorance with regard to their prevention in the general population. Further the preventive measures are not covered in the school curriculum. Objective: The study was done to provide information about the effectiveness of community-based health education on non communicable diseases among intermediate college students. Methods: The cross sectional study was carried out at Government Intermediate College. A health education programme of the intermediate class students was conducted. The impact was evaluated by comparing the pre and post test proformas filled by 133 students. The proforma consisted of 16 questions related to different non communicable diseases. Results: The 16 questions proforma was grouped 4 under categories. In pre test 35.5% correct answers were obtained which increased to 69.0% in the post test. (p = 0.0000). Significant improvement in knowledge was seen in all categories of questions which included Cardiovascular disease (p = 0.0000); hypertension (p = 0.0000); diabetes (p = 0.0000) and obesity (p = 0.0000). Conclusion: The findings of current study suggest that knowledge of students significantly improved after health education. Thus, health education programmes should regularly be conducted for improving the knowledge of students.
Keywords: Health Education, Non communicable diseases, Knowledge, College students
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SMMH Government Medical College, Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. Email: |
Kumar D, Vikramaditya B, Joshi HS, Jha AK, Manjeeta. Assessment of impact of health education on non communicable diseases on knowledge of intermediate college students. Public Health Rev Int J Public Health Res. 2019;6(2):76-81. Available From https://publichealth.medresearch.in/index.php/ijphr/article/view/103 |


 ©
©