Nursing Leadership Role in Pandemic
Pakhide V.1, Verma M.2*
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijphr.2021.i02.01
1 Vandana Pakhide, Associate Professor, Pragyan College of Nursing, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India.
2* Mamta Verma, Associate Professor, College of Nursing, AIIMS, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India.
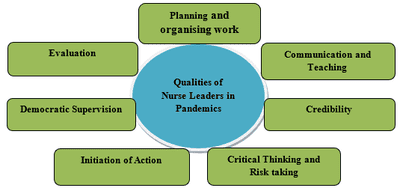
A Pandemic is an epidemic of disease that has spread across a large region, multiple continents or worldwide, COVID-19 is a large issue worldwide. A good nurse leader is someone who can inspire others to work together in pursuit of a common goal, such as enhanced patient care. An effective leader has a distinctive set of personal qualities; integrity, courage, initiative and an ability to handle stress, and also taking the effort to think critically, set goals and skilfully communicates and collaborate. Nurse’s leaders are faced with a variety of challenges in pandemics, including managing resources, advanced planning and goal setting, collaborating with other hospital and community leaders, improving quality measures, cost-effectiveness, reporting to the board of directors, and many more. Nurses as effective partners of the health care team, of necessity, have to meet the demands of these changes adequately and appropriately in respect of their expanded and enriched roles and responsibilities. Nurse leaders, however, are still confined within their nursing orbit, but, today they have to be visible and interactive members of the multi-disciplinary health team with a vision and voice that can be heard. Methods: For the present review article collected a database from Google scholar; search and scrutinize studies related to nurse’s leadership role during pandemic and article related to Covid-19 outbreak, government, community effort and mitigation strategies in reducing transmission. Result: Because it is a novel pandemic; results suggest that more researches are needed in this field related to driven factors, mitigation strategies and support of governmental and non-governmental organizations. This review article is aimed that nursing leaders must continue to develop plans that can slow or prevent the progress of widespread illnesses and ensures that all client care provided by the team is carried out in keeping with the objectives of the health care organisation.
Keywords: Leadership, Pandemic, Mitigation
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Associate Professor, College of Nursing, AIIMS, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. Email: |
Pakhide V, Verma M. Nursing Leadership Role in Pandemic. Public Health Rev Int J Public Health Res. 2021;8(2):07-12. Available From https://publichealth.medresearch.in/index.php/ijphr/article/view/154 |


 ©
©