Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among people attending medical camps in South Chennai, India
S. Anusuya G.1*, Gopalakrishnan S.2, Ravi R.3, Stephen T.4, Krishnakumar J.5, Ezhil R.6, Raja S.7, Yogaraj A.8
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijphr.2015.i4.02
1* Ganesh S. Anusuya, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital (SBMCH ), Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
2 Gopalakrishnan S, Professor & HOD, Department of Community Medicine, SBMCH, Bharath University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
3 Rama Ravi, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SBMCH, Bharath University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
4 Stephen T, Associate Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SBMCH, Bharath University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
5 Krishnakumar J, Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SBMCH, Bharath University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
6 Ezhil R, Technical Officer, National Institute of Epidemiology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
7 Raja S, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SBMCH, Bharath University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
8 Arunkumar Yogaraj, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, SBMCH, Bharath University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
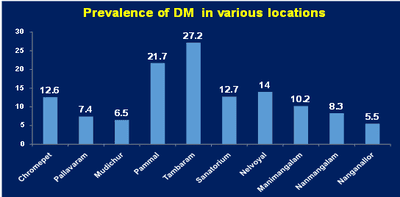
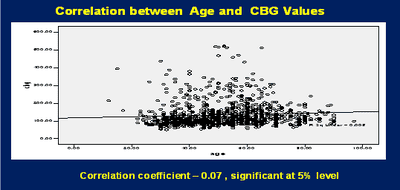
Background: As per the International Diabetes Federation (2013), nearly 65.1 million people were living in India with diabetes. Aim and Objectives: To estimate the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes and to compare the prevalence in relation to gender, age and area. Methodology: A cross- sectional record based study done on 1056 people attending medical camps conducted by Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital, in various locations of South Chennai. The data regarding Random Blood Sugar (RBS), age, gender and camp site were collected from the camp register (October 2014 to June 2015). Results: Among study population, 453 (42.9%) were males and 603 (57.1%) females. The overall prevalence of diabetes was 11.8%. Tambaram area showed highest prevalence of 27.3%. Prevalence in males (12.4%) versus females (11.4%) [p- 0.647], above 45 years (12.6%) versus below 45 years (10.4%) [p- 0.303], and urban (13.2%) versus rural (11%) [p- 0.291]. Conclusions: Prevalence of diabetes was 11.8% which is higher than the existing documented prevalence of 10.4%. Hence more awareness creation and preventive measures needs to be targeted in this population to reduce the disease burden.
Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Prevalence, South Chennai, RBS, Age
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital (SBMCH ), Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Email: |
Anusuya GS, Gopalakrishnan S, Ravi R, Stephen T, Krishnakumar J, Ezhil R, Raja S, Yogaraj A. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among people attending medical camps in South Chennai, India. Public Health Rev Int J Public Health Res. 2015;2(4):32-37. Available From https://publichealth.medresearch.in/index.php/ijphr/article/view/16 |


 ©
©