A cross sectional study on needle stick injuries, its associated factors and prophylactic measures among nursing staffs and students of a tertiary care hospital in Chennai
Rajesh J.1*, Thamizhmaran S.2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijphr.2019.i2.01
1* Rajesh J, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Government Medical Collegea, Omandurar Government Estate, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, Indiua.
2 S.P. Thamizhmaran, Final year MBBS student, Government Medical Collegea, Omandurar Government Estate, Chennai, Tamil Nadu , India.
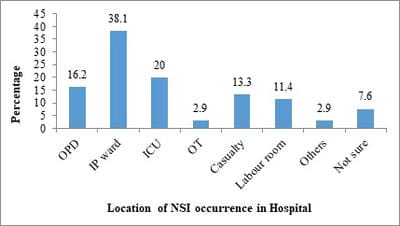
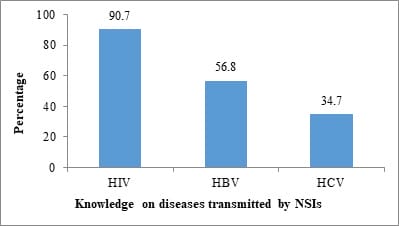
Introduction: Nurses have the highest rate of Needle Stick Injuries (NSIs) among health care workers. Objectives: 1. To determine the prevalence of NSIs in the past three months among nursing staffs and students of a Tertiary Care Hospital and the factors associated with it. 2. To assess the pre and post exposure prophylactic measures related to NSIs followed by them. Methodology: This cross-sectional study was conducted between May and June 2017 among 354 subjects including 218 staff nurses and 136 nursing students of a Tertiary Care Government Hospital in Chennai City. After the Institutional Ethics Committee approval, subjects were interviewed with a pre-designed semi structured questionnaire. Data was analysed using relevant descriptive and inferential statistics with trial version of SPSS.v.25.0 Results: Prevalence of NSIs in the past three months was 29.7% (n=105). Majority 79 (58.1%) nursing students had experienced NSIs. Two handed recapping of syringes was significantly associated with NSIs (P = 0.001, OR = 4.363, 95% C.I = 2.033 – 9.364). Around 40 (38.1%) of the NSIs had occurred most commonly at the In-patient wards. Majority 62 (59%) of them had never reported about their NSI while only 25 (23.8%) had reported regularly. Among those who got vaccinated with HBV vaccine (n = 57) for pre-exposure prophylaxis, only 13 (22%) had taken three doses of HBV. Conclusion: Two handed recapping of syringes, non-usage of gloves, lack of assistance and inattentiveness during procedures, especially among nursing students are the major associated factors for occurrence of NSIs.
Keywords: Needle Stick Injuries (NSIs), Post-exposure Prophylaxis (PEP), Recapping of syringes, Safe Injection practices.
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Government Medical Collegea, Omandurar Government Estate, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, Indiua. Email: |
Rajesh J, Thamizhmaran SP. A cross sectional study on needle stick injuries, its associated factors and prophylactic measures among nursing staffs and students of a tertiary care hospital in Chennai. Public Health Rev Int J Public Health Res. 2019;6(2):41-52. Available From https://publichealth.medresearch.in/index.php/ijphr/article/view/99 |


 ©
©