Impacts on dietary habits and health of Indian population during COVID-19 lockdown
Rajesh Kumar R.1, Arumugham Dhanaraj S.2*, Saini R.3, Kumari P.4, Roy P.5, Paul S.6
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijphr.2020.i06.01
1 Ramasamy Rajesh Kumar, Research Scientist, College of Agriculture and Biotechnology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
2* Saravanakumari Arumugham Dhanaraj, Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Government Villupuram Medical College, Villupuram, Tamilnadu, India.
3 Rashmi Saini, UG Student, Department of Home Science, Lady Irwin College, Delhi University, New Delhi, India.
4 Punita Kumari, Research Scholar, School of Material Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China.
5 Priyanka Roy, Research Scholar, National Institute of Food Technology Entrepreneurship and Management, Sonepat, Haryana, India.
6 Sayan Paul, Research Scholar, Department of Biotechnology, Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tirunelveli, Tamilnadu, India.
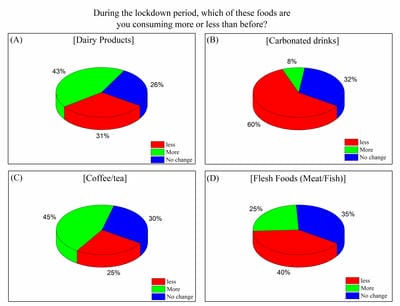
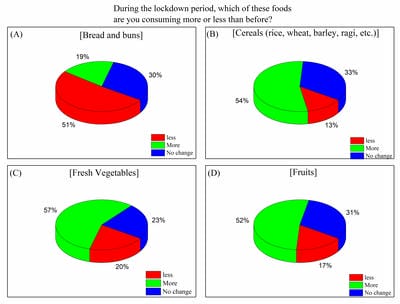
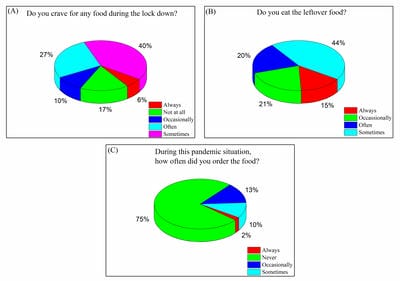
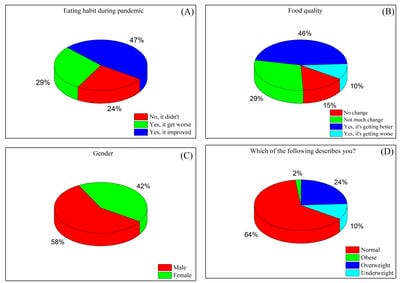
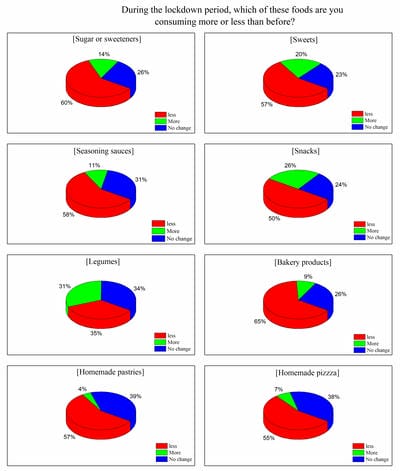
In late 2019 the outbreak of a novel infectious coronavirus (SARS CoV2) which became global pandemic and named as Coronavirus disease (CoViD-19) World Health Organization (WHO). On 22 March, 2020 the Prime Minister of India announced and 14 hours’ public curfew and from 24 March, 2020 announced sudden complete lockdown. The sudden complete lockdown made changes in the living habits and social behaviors of public. Web based survey was conducted among the Indian population of different age groups to understand the impacts on dietary habits and health during the sudden complete lockdown in India.
Keywords: Dietary habits, Health, India, COVID19, Pandemic, Lockdown
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Government Villupuram Medical College,Villupuram, Tamilnadu, India Email: dr.saravanakumari@gmail.com |
Kumar RR, Dhanaraj SA, Saini R, Kumari P, Roy P, Paul S. Impacts on dietary habits and health of Indian population during COVID-19 lockdown. Public Health Rev Int J Public Health Res. 2020;7(6):38-50. Available From https://publichealth.medresearch.in/index.php/ijphr/article/view/143 |


 ©
©