A cross sectional study to assess the socio-economic impact of falls in an urban community in South India
Vani CH.1*, Nandakumar B S.2, Murthy N S.3, Suryanarayana S. P.4
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijphr.2016.i4.03
1* Vani CH, Department of Community Medicine, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
2 Nandakumar B S, Department of Community Medicine, M. S. Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
3 Murthy N S, Department of Community Medicine, M. S. Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
4 Suryanarayana S. P., Department of Community Medicine, M. S. Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
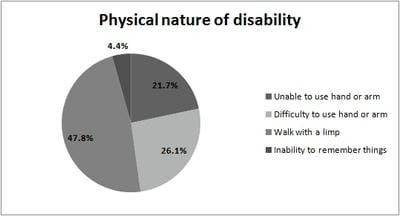
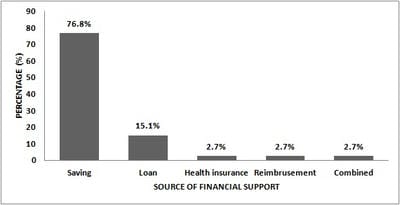
Background: Epidemiological transition have resulted the injuries to emerge as a global public health problem. Falls are one of the leading causes of injuries and has been predicted that it will be top 20 leading cause of death by 2030. Very few studies have been conducted about falls in all age groups. Hence the present study focussed on the prevalence of falls in an urban area, Bangalore and its social and economic impact on the individual and their family. Materials and Methods: Cross sectional study was conducted covering 3003 population by house-house survey. Pre-tested, semi-structured questionnaire was used. Among injured by falls further details was obtained. Results: Prevalence of falls was 23/1000 population; 95% CI (18-29). High prevalence was seen among extremes of age group and among males. Home was the common place of falls. Lower limb was common injury site and fracture was seen in 16.4% cases. Even after one month of injury, disability persisted in 31.5% cases. Hospital charges were high for elderly people (P=0.04). Total cost incurred following falls was high among 15-59 year age group (P=0.005). Conclusions: Prevalence of falls was 23/1000 population; 95% CI (18-29). Social impact in terms of disability lasting even after one month following falls was present in 31.5%, most common being limping. Though the prevalence of falls was high among extremes of age group, overall economic impact following falls was high among 15-60 year age group.
Keywords: Cost, Disability, Falls, Socio-economic impact, Urban area
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , , Department of Community Medicine, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India. Email: |
Vani CH, Nandakumar B S, Murthy N S, Suryanarayana S P. A cross sectional study to assess the socio-economic impact of falls in an urban community in South India. Public Health Rev Int J Public Health Res. 2016;3(4):156-161. Available From https://publichealth.medresearch.in/index.php/ijphr/article/view/45 |


 ©
©