A study on socio-demographic factors of alcoholics attending a deaddiction centre in Kannur district
Abstract
Background: Alcoholism is a major public health problem in Kerala. It leads to serious social, mental and physical consequences.
Method: A deaddiction centre based cross sectional study was done on 370 individuals using a predesigned questionnaire during the period of 2012-2013. The data was analyzed using SPSS version 17. Chi – Square test was used to find association between the study variables.
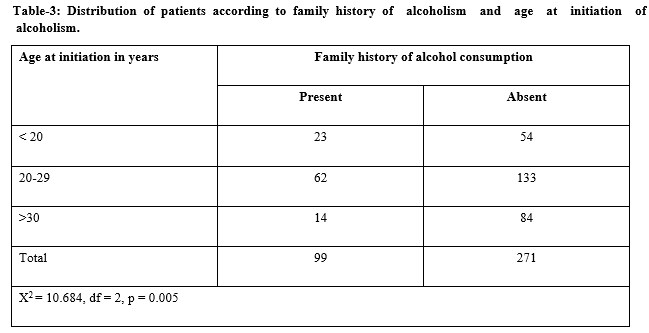
Results: The study was done on 370 alcohol dependent subjects. The mean age of the study subjects was 38.08±8.46 years. 64.3% of the study subjects were from rural areas. The mean age of starting alcohol consumption was 25.46±6.6 years. Family history of alcohol consumption was present in 99 (26.8%) patients. The age at initiation of alcohol intake was significantly (p < 0.05) associated with family history. The mean duration of drinking was 12.62±7.47 years. 42.4% of the study subjects consumed brandy. 37.6% of them consumed < 200ml of alcohol per day. Peer pressure was the most common reason cited by 44.1% individuals for starting alcohol consumption. The most common reason cited by 30.5% individuals for continuing alcohol consumption was because they liked its effect. Family problems and financial problems were the most common reasons cited wanting to stop alcohol consumption.
Conclusion: Alcohol use is a serious public health problem. Awareness programs regarding its harmful use should be given to the people in the community.
Downloads
References
2. WHO launches SAFER alcohol control initiative to prevent and reduce alcohol-related death and disability. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/28-09-2018-who-launches-safer-alcohol-control-initiative-to-prevent- and- reduce- alcohol-related-death-and-disability
3. WHO. Health situation in South East Asia Region, 2001-2007. Available at: http:// apps.searo.who.int/pds_ docs / B3226.pdf
4. Park K. Nutrition and Health, Park's Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine. Banarsidas Bhanot Publishers. 2017;1167:561-617.
5. Ranaweera S. Current information on use and harm from alcohol in the WHO South East Asia Region. Alcohol control series No. 6. WHO Press; 2007. Available at: http:// apps.searo.who.int/ PDS_DOCS / B0572. pdf
6. Gururaj G, Girish N, Benegal V, Chandra V, Pandav R. Public health problems caused by harmful use of alcohol- gaining less or losing more? (Alcohol control series No.2). New Delhi: Macro Graphics Pvt Ltd; 2006. p.9-10.
7. Alcoholic beverages consumed in Kerala 2010.
8. Gururaj G, Girish N, Benegal V, Chandra V, Pandav R. Burden and socioeconomic impact of alcohol, The Bangalore Study. World Health Organization, South East Asia Regional office, New Delhi. 2006.
9. Suryakantha AH. Biostatistics. Community Medicine (With Recent Advances). New Delhi:Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd;2009.p.628.
10. Dudala SR, Arlappa N. An updated Prasad’s socioeconomic status classification for 2013. Int J Res Dev Health. 2013;1(2):26-28.
11. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. Available at: http://www. who. int/classifications/icd/en/bluebook.pdf.
12. Saxena S. Country profile alcohol India. In: Leanne Riley, Mac Marshall. Alcohol and public health in eight developing countries. WHO Geneva: Substance abuse department social change and mental health; 1999. Available at: http:// apapaonline. org/data/National_ Data / India/Country_Profile_Alcohol_India.pdf.
13. Sarkar AP, Sen S, Mondal S, Singh OP, Chakraborty A, Swaika B. A study on socio-demographic characteristics of alcoholics attending the de-addiction center at Burdwan medical college and hospital in West Bengal. Indian J Public Health. 2013; 57 (1):33-35. doi: 10.4103/0019-557X.111366.
14. Pradeep RJ, Banu S, Ashok MV. Severity of alcoholism in Indian males: correlation with age of onset and family history of alcoholism. Indian J Psychiatry. 2010; 52(3): 243-249. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545. 70977
15. Meena PK, Vohra AK, Rajput R. Prevalence and pattern of alcohol and substance abuse in urban areas of Rohtak city. Ind J Psychiat. 2002;44(4):348-352.
16. Girish N, Kavita R, Gururaj G, Benegal V. Alcohol use and implications for public health: patterns of use in four communities. Indian J Comm Med: Indian Association of Prevent Social Medi. 2010; 35(2):238. doi: 10.4103/0970-0218.66875.
17. Vignesh BT, Singh AK, Mohan SK, Murthy S, Joshi A. Association between socio-demographics and alcohol dependence among individuals living in an Indian setting. Global J Health Sci. 2014;6(3):16-26. doi: 10.5539/gjhs.v6n3p16.
Copyright (c) 2019 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


