Parental Engagement and Adolescents Mental Health Wellbeing: Cross-Sectional Study from Sri Lanka
Abstract
Background: Parental engagement is one of the key factors that can influence adolescents mental health status, although these associations are not fully measured in the local context. This study will estimate the prevalence and association of parental engagement with adolescents and mental health status in Sri Lanka.
Method: This current study is a secondary analysis of nationally representative data for Sri Lanka. The data was collected from 3262 school attending students in grades 8-12 in the Sri Lankan Global School-based health survey (GSHS) 2016. A two-stage cluster sample design was used to select the representation of samples. The binary variables i.e. loneliness, anxiety and suicidal ideation, were modelled using multivariable logistic regression models with predictors representing gender, age, grade, parental supervision and parental understanding.
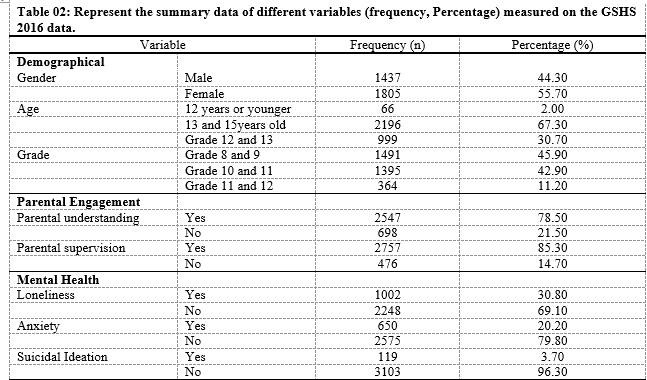
Result: It is estimated that the prevalence of parental supervision and parental understanding is 85.3% and 78.5%, respectively. The analysis of both good parental supervision and parenting understanding has reduced the loneliness, anxiety and suicidal thoughts among the adolescents population, compared to those who don't have good parental engagement.
Conclusion: It is seen that there is a higher prevalence of parental and children engagement in Sri Lanka compared to other demographical regions. However, the prevalence of mental health remains higher as compared to the global average. The results suggest that national policies and programs should be integrated for both parents and children. Parents need more knowledge on good parenting, while adolescents need support on coping with their mental health.
Downloads
References
Newman K, Harrison L, Dashiff C, Davies S. Relationships between parenting styles and risk behaviors in adolescent health: an integrative literature review. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2008 Jan-Feb;16(1):142-50. doi: 10.1590/s0104-11692008000100022.
Cripps, Kayla, and Brett Zyromski. "Adolescents' psychological wellbeing and perceived parental involvement: Implications for parental involvement in middle schools." RMLE Online 33.4 (2009): 1-13.
Kieling, Christian, et al. "Child and adolescent mental health worldwide: evidence for action." The Lancet 378.9801 (2011): 1515-1525.
Fotti, S. A., Katz, L. Y., Afifi, T. O., & Cox, B. J. The associations between peer and parental relationships and suicidal behaviours in early adolescents. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 51.11 (2006): 698-703.
Kerr M, Stattin H, Trost K. To know you is to trust you: parents' trust is rooted in child disclosure of information. J Adolesc. 1999 Dec;22(6):737-52. doi: 10.1006/jado.1999.0266.
Fröjd, Sari, Riittakerttu Kaltiala-Heino, and Matti Rimpelä. "The association of parental monitoring and family structure with diverse maladjustment outcomes in middle adolescent boys and girls." Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 61.4 (2007): 296-303.
Bireda, Asamenew Demessie, and Jace Pillay. "Perceived parental involvement and wellbeing among Ethiopian adolescents." Journal of Psychology in Africa 27.3 (2017): 256-259.
Rudatsikira, E., Siziya, S., Kazembe, L. N., & Muula, A. S. Prevalence and associated factors of physical fighting among school-going adolescents in Namibia. Annals of General Psychiatry, 6.1 (2007): 1-5.
Hasumi, T., Ahsan, F., Couper, C. M., Aguayo, J. L., & Jacobsen, K. H. Parental involvement and mental wellbeing of Indian adolescents. Indian pediatrics, 49.11 (2012): 915-918.
Pathirana, Buddhiprabha DD. "Sri Lankan adolescents' relationships with their parents, siblings and peers: an exploratory study." The International Journal of Indian Psychology 3.2 (2016): 38-50.
Ministry of Health SL. Ministry of Health, Nutrition and Indigenous Medicine Sri Lanka [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2020 Jul 19]. Available from: www.health.gov.lk
Hasumi T, Ahsan F, Couper CM, Aguayo JL, Jacobsen KH. Parental involvement and mental wellbeing of Indian adolescents. Indian Pediatr [Internet]. 2012 Nov 10 [cited 2021 Jan 31];49(11):915–8. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13312-012-0218-y
Nguyen, H. T. L., Nakamura, K., Seino, K., & Al-Sobaihi, S. Impact of parent–adolescent bonding on school bullying and mental health in Vietnamese cultural setting: evidence from the global school-based health survey. BMC psychology, 7.1 (2019): 1-10.
Murshid NS. Bullying victimization and mental health outcomes of adolescents in Myanmar, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2017 May 1;76:163–9.
WHO. Sri Lanka - Global School-based Student Health Survey 2016 [Internet]. 2016. [cited 2020 Jul 11]. Available from: https://nada.searo.who.int/index.php/catalog/8/related_materials
Becker, A. E., Roberts, A. L, Perloe, A., Bainivualiku, A., Richards, L. K., Gilman, S. E., et al. Youth health-risk behavior assessment in Fiji: the reliability of Global School-based Student Health Survey content adapted for ethnic Fijian girls. Ethnicity & health, 15.2 (2010): 181-197.
Pengpid S, Peltzer K. Parental involvement and mental health among school-going adolescents in five Caribbean countries. J Psychol Africa [Internet]. 2018 Sep 3 [cited 2021 Feb 4];28(5):394–9. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14330237.2018.1501916
Murray, Christopher JL. "The global burden of disease: a comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from diseases, injuries, and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020." Global burden of disease and injury series (1990).
Astbury, Jill. "Gender disparities in mental health." (2001): 73-92.
Qualter, P., Brown, S. L., Munn, P., & Rotenberg, K. J. Childhood loneliness as a predictor of adolescent depressive symptoms: an 8-year longitudinal study. European child & adolescent psychiatry, 19.6 (2010): 493-501.
Edwards, C. P., W. Liu, and M. H. Bornstein. "Handbook of parenting: Vol. 1. Children and parenting." (2002): 45-71.
Stickley, A., Koyanagi, A., Koposov, R., Blatný, M., Hrdlička, M., Schwab-Stone, M., et al. Loneliness and its association with psychological and somatic health problems among Czech, Russian and US adolescents. BMC psychiatry, 16.1 (2016): 1-11.
Biederman, J., Petty, C. R., Hirshfeld-Becker, D. R., Henin, A., Faraone, S. V., Fraire, M, et al. Developmental trajectories of anxiety disorders in offspring at high risk for panic disorder and major depression. Psychiatry research, 153. 3(2007): 245-252.
Li, Xinjun, Jan Sundquist, and Kristina Sundquist. "Age-specific familial risks of anxiety." European archives of psychiatry and clinical neuroscience 258.7 (2008): 441-445.
Drake, Kelly L., and Golda S. Ginsburg. "Parenting practices of anxious and nonanxious mothers: A multi-method, multi-informant approach." Child & Family Behavior Therapy 33.4 (2011): 299-321.
Dornbusch, S. M., Ritter, P. L., Leiderman, P. H., Roberts, D. F., & Fraleigh, M. J. The relation of parenting style to adolescent school performance. Child development (1987): 1244-1257.
Steinberg, Laurence, Julie D. Elmen, and Nina S. Mounts. "Authoritative parenting, psychosocial maturity, and academic success among adolescents." Child development (1989): 1424-1436.
Wei C, Kendall PC. Parental Involvement: Contribution to Childhood Anxiety and Its Treatment. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev [Internet]. 2014;17(4):319–39. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-014-0170-6
Jordans MJD, Kaufman A, Brenman NF, Adhikari RP, Luitel NP, Tol WA, et al. Suicide in South Asia: A scoping review. BMC Psychiatry [Internet]. 2014 Dec 24 [cited 2021 Jan 24];14(1):358. Available from: http://bmcpsychiatry.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12888-014-0358-9
Knipe DW, Gunnell D, Pearson M, Jayamanne S, Pieris R, Priyadarshana C, et al. Attempted suicide in Sri Lanka - An epidemiological study of household and community factors. J Affect Disord. 2018 May;232:177-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.01.028.
Rajapakse, T., Griffiths, K. M., Christensen, H., & Cotton, S. Non-fatal self-poisoning in Sri Lanka: associated triggers and motivations. BMC public health, 15.1 (2015): 1-7.
Thalagala N. Suicide Trends in Sri Lanka 1880-2006; Social, Demographic and Geographical Variations. J Coll Community Physicians Sri Lanka [Internet]. 2011 Apr 8 [cited 2021 Jan 24];14(1):24. Available from: https://jccpsl.sljol.info/article/10.4038/jccpsl.v14i1.2945/
UNESCO. New education data for SDG4: Focus on out-of-school children, 27 September 2018 | Education within the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [Internet]. 2018. [cited 2020 Jul 6]. Available from: https://www.sdg4education2030.org/new-education-data-sdg4-focus-out-school-children-27-september-2018
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


