Health behaviors changes during COVID-19: a study of Australianimmigrants
Abstract
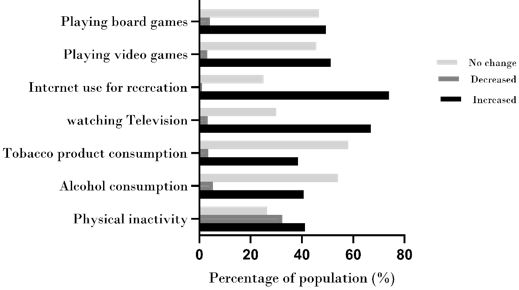
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic has disproportionately affected different immigrant groups.The increase in health risk factors in times of COVID-19 has been under-researched, among theimmigrant population of Australia. Objectives: This study aimed to investigate changes in healthbehaviors during COVID-19 in South Asian Australian immigrants. Methods: An 2020 and March 2tobacco and alcohol consumption, internet,and board games use for recreation.Result: Most immigrants (40.7%) reported an increase inalcohol consumption while only 5.3% reported a decrease. Tobacco use increased by 38.5 % whiledecreased by 3.5%. The increase in watching television (66.8%) and internet use for recreation(73.9%) were also noticeable. Physical inactivity increased in 41.1% of the participants anddecreased in 32.4%. Participants from the high-income group were significantly associated with anincrease in physical inactivity, alcohol consumption, and playing video games (p<0.005). Conclusions: Longitudinal tracking is required to understand the effect of these changes in healthbehaviors and their health consequences in the immigrant population of Australia
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2022 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


