Prevalence of hypertension and its risk factors among adults in central Kerala
Abstract
Introduction: High blood pressure is both preventable and treatable. Community based studies on the prevalence of hypertension is now necessary to assess the prevalence of hypertension & its risk factors. Epidemiological studies to assess the prevalence of hypertension are essential to plan preventive strategies & promote the health of population. A study of the prevalence of hypertension among adults (>19 years), the association between socio-demographic and behavioral risk factors in hypertension and the treatment seeking behavior in the population in Thrissur district of Kerala was conducted.
Methods: In this community based cross sectional study, 740 adults were studied for 1 year. The sampling technique used was Multi Stage Cluster sampling. Using standard questionnaire and interview, information was collected. Blood pressure was measured twice in each subject using a mercury sphygmomanometer adopting standardized techniques and their averages were taken.
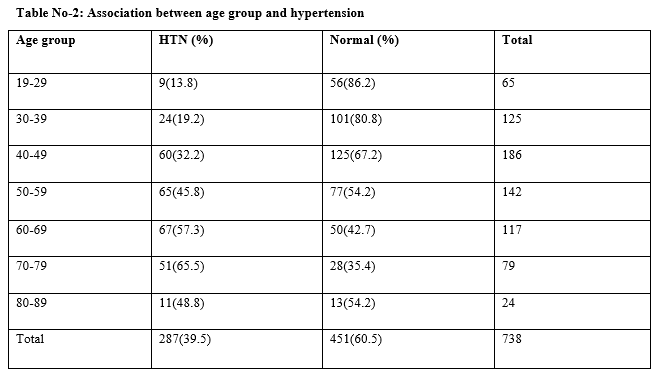
Results: Maximum prevalence of hypertension was in the age group 50-69 years, showing increasing trend after 40 years onwards. Of the hypertensives 43.9% were males. Among the hypertensive group, 227(79%) had an educational qualification of 12th standard and below. Statistically significant associations of hypertension were found with educational status and BMI.
Conclusion: We conclude that age group and education status were associated with hypertension.
Downloads
References
2. T, Reddy KS, Paccaud F, Horton S, Chaturvedi V. Cardiovascular disease. In: Jamison DT, Mosley WH, editors. Disease Control Priorities in the Developing World. Oxford: oxford university press; 2006. Pp. 645 – 62.
3. Gupta R. Trends in hypertension epidemiology in India. J Hum Hypertens. 2004 Feb;18(2):73-8.
4. Padmavati S. A meta- analysis- National Heart Institute, New Delhi. Ind Heart J 2002: 54: 99-104.
5. Weber MA, Schiffrin EL, White WB et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension in the Community A Statement by the American Society of Hypertension and the International Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2014 Jan;32(1):2.
6. Hypertension Study Group. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension among the elderly in Bangladesh and India: a multicentre study. Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79(6):490-500.
7. S. Anil Bindhu, Nazeema Beevi, Thankam.K, V.Girija, Jeesha C Haran. Prevalence and Determinants of Hypertension among Adults in A Rural Area in Thirvananthapuram, Kerala-A Cross Sectional Study. In: International Journal of Medical and Applied Sciences. 2014; Vol3 issue1.
8. Addo J, Agyemang C, Smeeth L, de-Graft Aikins A, Edusei AK, Ogedegbe O. A review of population-based studies on hypertension in Ghana. Ghana Med J. 2012 Jun;46(2 Suppl):4-11.
9. Gupta R, Guptha S, Gupta VP, Prakash H. Prevalence and determinants of hypertension in the urban population of Jaipur in western India. J Hypertens. 1995 Oct;13(10):1193-200.
10. Wang W, Lee ET, Fabsitz RR, Devereux R, Best L, Welty TK, Howard BV. A longitudinal study of hypertension risk factors and their relation to cardiovascular disease: the Strong Heart Study. Hypertension. 2006 Mar;47(3):403-9. Epub 2006 Jan 23.
11. Laxmaiah A, Meshram II, Arlappa N, Balakrishna N, Rao KM, Reddy ChG, Ravindranath M, Kumar S, Kumar H, Brahmam GN. Socio-economic & demographic determinants of hypertension & knowledge, practices & risk behaviour oftribals in India. Indian J Med Res. 2015 May;141(5):697-708.
12. Wamala JF, Karyabakabo Z, Ndungutse D, Guwatudde D. Prevalence factors associated with hypertension in Rukungiri district, Uganda--a community-based study. Afr Health Sci. 2009 Sep;9(3):153-60.
13. Hypertension in Diabetes Study (HDS): I. Prevalence of hypertension in newly presenting type 2 diabetic patients and the association with risk factors for cardiovascular and diabetic complications. J Hypertens. 1993 Mar;11(3):309-17.
14. Fagard RH. Physical activity in the prevention and treatment of hypertension in the obese. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999 Nov;31(11 Suppl):S624-30.
15. Halbert JA, Silagy CA, Finucane P, Withers RT, Hamdorf PA, Andrews GR. The effectiveness of exercise training in lowering blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of 4 weeks or longer. J Hum Hypertens. 1997 Oct;11(10):641-9.
16. Appel LJ, Brands MW, Daniels SR, Karanja N, Elmer PJ, Sacks FM; American Heart Association. Dietary approaches to prevent and treat hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2006 Feb;47(2):296-308.
17. Ha SK. Dietary salt intake and hypertension. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2014 Jun;12(1):7-18. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2014 .12.1.7. Epub 2014 Jun 30.
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


